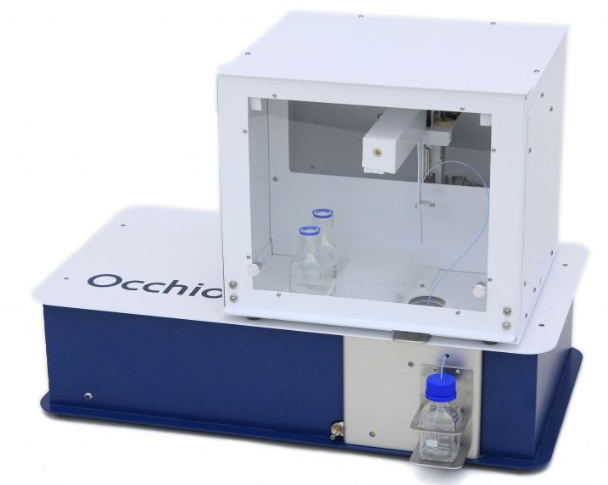
Ipac 2 AR
The IPAC2 AR has been designed for and tested to be the newer and faster AST method.
With the IPAC2 AR, it is possible to determine the concentration of bacteria present in a liquid solution. The image analysis-based instrument counts the number of particles (ranging from 0.3 µm to 1000 µm). Because of these features, the IPAC2 AR can be used to quantify bacteria.
Over the past years antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) methods have become essential for the treatment and control of infectious diseases caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria. With these testing methods doctors are able to choose the correct antibiotic and thereby ensure a better treatment for patients.
However, despite their importance, the conventional AST methods (disk diffusion and photometry) are time consuming and can take up to 48 hours. The Ipac2 AR is the newer and faster AST method as seen in the supporting graphs.
The application of the IPAC2 AR to quantify bacterial growth, makes it suitable as a new method for performing an antimicrobial susceptibility test. In the incubation chamber of the IPAC2 AR bacteria can be grown at the correct temperature (37°C).
At desired timepoints, the automated dispensing robot takes a sample of the growing bacteria and determines the concentration. Using a 96-deepwell plate bacterial growth of different strains can be quantified in the presence and absence of several antibiotics.
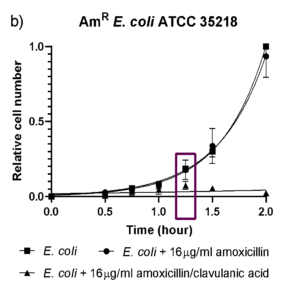
A study was performed using the IPAC2 AR to quantify growth of Escherichia coli (E. coli) ATCC 25922 and amoxicillin resistant E. coli ATCC 35218 in the presence and absence of amoxicillin (16 µg/ml) and amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (16 µg/ml; ratio 2:1).
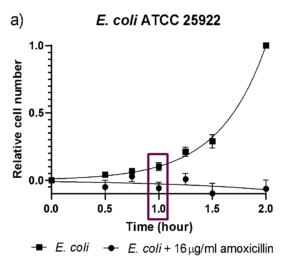
- The antimicrobial susceptibility growth test showed exponential growth of E. coli ATCC 25922 after 1 h (p ≤ 0.05, n ≥ 3), while there was no growth in the presence of amoxicillin.
This demonstrates that the IPAC2 AR can identify susceptibility of E. coli for amoxicillin already after 1h.
-
For amoxicillin resistant E. coli ATCC 35218, susceptibility for amoxicillin/clavulanic acid was observed after 1.25 h (p ≤ 0.05, n ≥ 3), while there was still growth in the presence and absence of amoxicillin. These results demonstrate resistance of the E. coli for amoxicillin and susceptibility for amoxicillin in the presence of clavulanic acid after 1.25 h.
In this proof-of-principle study using E. coli and the IPAC2 AR, resistance was detected at least 5 hours sooner compared to the conventional antibiotic susceptibility tests. Similar results were obtained for other bacteria (Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 700603 and (methicillin-resistant) Staphylococcus aureus) and antibiotics (oxacillin and erythromycin).